How to Sleep Better
How to Sleep Better: Mastering the Science of Better Sleep
Introduction:
In our fast-paced world, where screens flicker late into the night and stress levels soar, the elixir of quality sleep often feels elusive. Yet, it remains the cornerstone of a healthy lifestyle, influencing everything from our mood to our cognitive function. So, how can we reclaim the lost art of restful slumber? Here, we delve into the science-backed strategies to help you achieve that blissful state of rejuvenation every night.
Understanding the Importance of Sleep:
Before delving into the ‘how,’ let’s briefly touch on the ‘why.’ Sleep isn’t just a period of rest; it’s a critical process that allows our bodies and brains to recharge. During sleep, our brains consolidate memories, process emotions, and flush out toxins, while our bodies repair tissues and regulate hormones. Consistently poor sleep, on the other hand, has been linked to a myriad of health issues, including obesity, diabetes, and cardiovascular disease.
Establishing a Sleep-Friendly Environment:
Creating the right environment is paramount to promoting better sleep. Start by optimizing your bedroom for restfulness. Keep it cool, quiet, and dark, investing in blackout curtains if necessary. Ensure your mattress and pillows provide adequate support and comfort. Additionally, banish electronic devices from the bedroom, as the blue light emitted can disrupt your body’s natural sleep-wake cycle.
Developing a Consistent Sleep Schedule:
Our bodies thrive on routine, and sleep is no exception. Aim to go to bed and wake up at the same time every day, even on weekends. This helps regulate your body’s internal clock, making it easier to fall asleep and wake up naturally. Avoid the temptation to “catch up” on lost sleep by sleeping in excessively on weekends, as this can throw off your sleep schedule and lead to further sleep disturbances.
Mindful Consumption of Stimulants:
Certain substances can wreak havoc on our sleep patterns. Limit your intake of caffeine, especially in the afternoon and evening, as it can linger in your system for hours, disrupting sleep. Similarly, avoid heavy meals, nicotine, and alcohol close to bedtime, as they can all interfere with the quality of your sleep.
Managing Stress and Anxiety:
Stress and anxiety are among the most common culprits behind poor sleep. Incorporate stress-reducing practices into your daily routine, such as mindfulness meditation, deep breathing exercises, or journaling. If worries keep you awake at night, try jotting them down before bed to clear your mind.
Embracing Technology for Better Sleep:
While technology can sometimes disrupt sleep, it can also be harnessed to promote better sleep. Consider using sleep-tracking apps or wearable devices to monitor your sleep patterns and identify areas for improvement. Some apps also offer guided meditation or white noise features to help you drift off to sleep more easily.
Seeking Professional Help When Needed:
If you’ve tried various strategies to improve your sleep without success, don’t hesitate to seek help from a healthcare professional. Sleep disorders such as insomnia, sleep apnea, and restless leg syndrome are common and treatable. A healthcare provider can help diagnose underlying issues and recommend appropriate treatment options.
Why Sleep is Important ?
Sleep isn’t just a luxury; it’s a fundamental necessity for overall well-being. During sleep, our bodies repair tissues, regulate hormones, and consolidate memories. Adequate sleep is crucial for cognitive function, mood regulation, and immune system strength. Conversely, chronic sleep deprivation can lead to cognitive impairment, mood disorders, and increased risk of chronic diseases like obesity and heart disease. Prioritizing sleep is essential for optimizing physical and mental health. By establishing consistent sleep patterns, creating a conducive sleep environment, and practicing relaxation techniques, we can unlock the myriad benefits of quality sleep. Let’s recognize sleep as a cornerstone of health and wellness, prioritizing it alongside diet and exercise for a happier, healthier life.
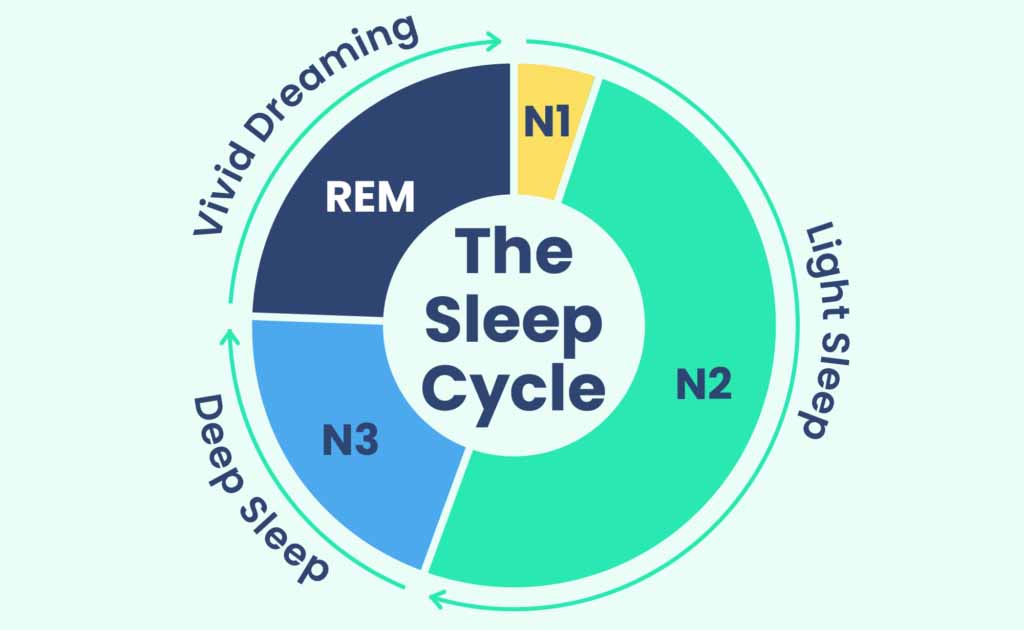
Sleep Cycles
Image Credit-sleepfoundation.org
Sleep cycles consist of distinct stages, each serving a unique purpose in our restorative process. We typically progress through four to five cycles per night, each lasting around 90 minutes. The stages include light sleep, deep sleep, and REM (rapid eye movement) sleep. During REM sleep, our brains are active, and vivid dreaming occurs. This cycle repeats throughout the night, with REM stages lengthening towards morning. Disruptions to these cycles can lead to sleep disturbances and affect overall sleep quality. Understanding and optimizing our sleep cycles is key to achieving restful and rejuvenating sleep.
In the sleep cycle, N1, N2, and N3 represent different stages of non-REM (rapid eye movement) sleep, each with distinct characteristics:
- N1 (Stage 1): N1 is the transitional stage between wakefulness and sleep. During this stage, brain waves begin to slow down, and muscle activity decreases. People in N1 may experience drifting in and out of consciousness, and it’s common to experience sudden muscle contractions known as hypnic jerks. This stage typically lasts for a few minutes.
- N2 (Stage 2): N2 is a deeper stage of sleep where the body prepares for deeper sleep. Brain waves continue to slow, and eye movements cease. During N2, the body temperature drops, and heart rate and breathing become more regular. This stage occupies the majority of our sleep cycle, accounting for about 45-55% of total sleep time.
- N3 (Stage 3): N3, also known as slow-wave sleep (SWS) or deep sleep, is the deepest and most restorative stage of sleep. During N3, brain waves slow down even further, and it becomes difficult to awaken. This stage is characterized by slow delta waves on EEG (electroencephalogram) readings. N3 is crucial for physical restoration, hormone regulation, and memory consolidation. It’s typically harder to awaken someone from N3, and if woken, they may feel groggy or disoriented. N3 usually occurs in the first half of the night and decreases as the night progresses.
These stages of non-REM sleep are essential for overall restorative sleep and contribute to physical and cognitive health. Disruptions to these stages can lead to sleep disturbances and impact overall sleep quality.
Quick Tips for Falling Asleep Faster
Struggling to fall asleep can be frustrating, but there are simple strategies to help you drift off into slumber more quickly. Here are some effective tips:
- Create a Relaxing Environment: Make your bedroom conducive to sleep by keeping it cool, dark, and quiet. Invest in comfortable bedding and pillows to enhance comfort.
- Establish a Bedtime Routine: Develop a pre-sleep routine to signal to your body that it’s time to wind down. This could include activities like reading, gentle stretching, or taking a warm bath.
- Limit Screen Time: Minimize exposure to electronic devices before bed, as the blue light emitted can disrupt your body’s natural sleep-wake cycle. Aim to avoid screens at least an hour before bedtime.
- Practice Relaxation Techniques: Incorporate relaxation techniques such as deep breathing, progressive muscle relaxation, or meditation to calm your mind and body before sleep.
- Manage Stress: Address any sources of stress or anxiety that may be keeping you awake. Engage in stress-reducing activities throughout the day, and consider journaling or making a to-do list before bed to clear your mind.
- Watch Your Diet: Avoid heavy meals, caffeine, and alcohol close to bedtime, as they can interfere with your ability to fall asleep. Opt for light snacks if you’re hungry before bed.
By implementing these tips and making sleep a priority, you can improve your ability to fall asleep quickly and enjoy a more restful night’s sleep.
Conclusion
In conclusion, achieving better sleep is not an elusive dream but a tangible goal within reach. By implementing the science-backed strategies discussed, such as creating a conducive sleep environment, establishing consistent sleep schedules, managing stress, and practicing relaxation techniques, you can pave the way for restorative and rejuvenating slumber. Remember, prioritizing sleep is not a luxury but a necessity for overall health and well-being. By making sleep a non-negotiable priority in your daily routine, you can unlock the countless benefits of quality rest, from improved cognitive function and mood to enhanced physical health and resilience. So, tonight, embrace the art of slumber, knowing that a good night’s sleep is truly the foundation of a healthier, happier life.